Obesity
Obesity is a multifactorial pathological condition characterized by a low-grade systemic inflammation (meta-inflammation), that seems to be a common root to the onset and progression of several obese-related comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
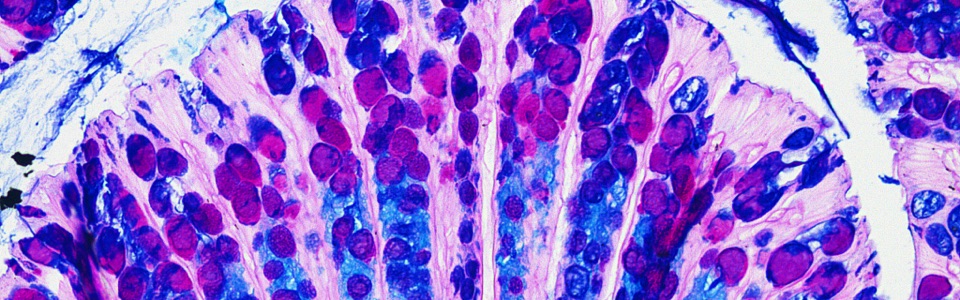
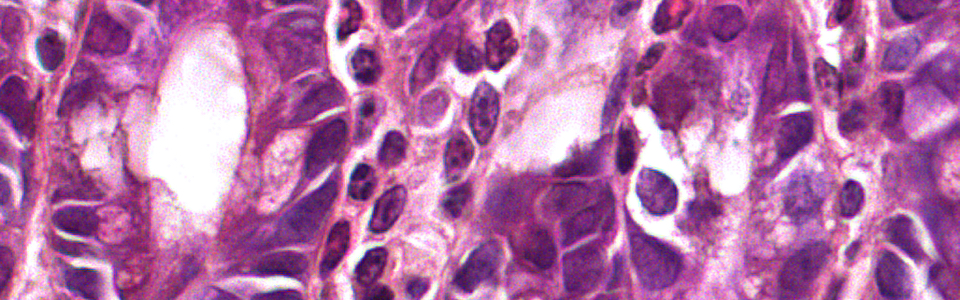
Obese patients often complain chronic gastrointestinal disturbances, including gastroesophageal reflux, diarrhea and constipation, which impact negatively on patients’ quality of life. In this context, changes in gut microbiota and its metabolites, the short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), have been identified among the main factors influencing early inflammatory events associated with obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Indeed, the presence of an imbalanced gut microbiota composition represent prodromal events eliciting fluctuations in the intestinal epithelial barrier integrity, thereby facilitating the translocation of immunogenic products (i.e. lipopolysaccharide, peptidoglycan, whole bacteria, and other toxins) in the enteric lamina propria and the bloodstream, triggering the onset and maintenance of a meta-inflammation typically observed in obese subjects.
Our research is focused on: 1) the characterization of the molecular pathway underlying the onset and development of obesity and related disorders, and 2) studies the effects resulting from the dietary supplementation with probiotics or natural mixture in counteracting the development of obesity and related comorbidities.
Our research focuses on three main areas:
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying obesity
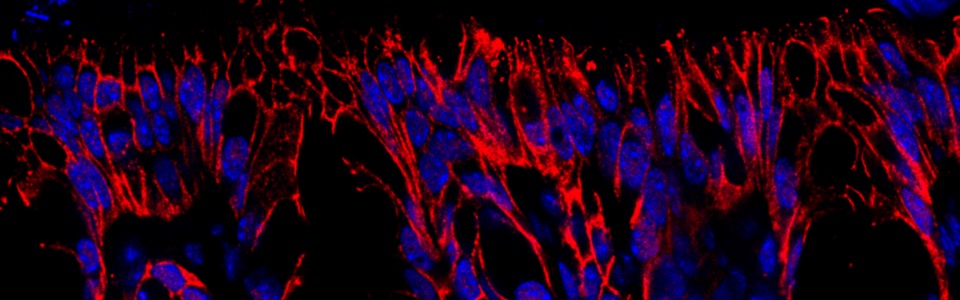
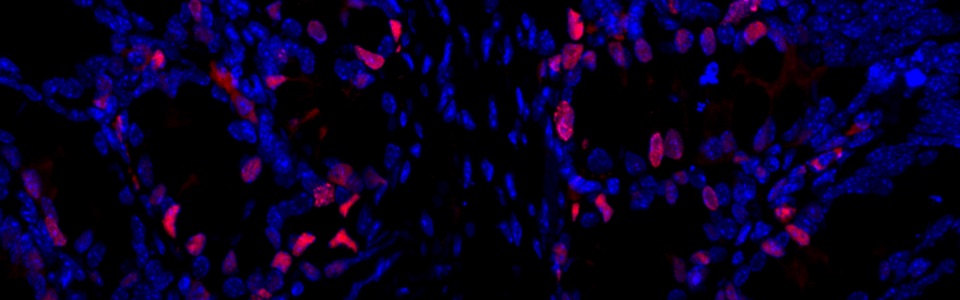
We are currently investigating the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the onset and development of obesity in experimental models of high fat-diet (HFD) induced obesity. In particular, our attention is focused on the role of alterations in gut microbiota, gut barrier, including mucus layer, intestinal epithelial barrier and glial cells in trigging the inflammatory processes and, consequently, the neuroplastic changes in the enteric nervous system.
-
Novel therapeutical approaches
We are currently characterizing the effects of probiotics and natural mixtures in our murine models of obesity.
-
Translational studies
We are currently studying changes in gut microbiota and its metabolites as well as inflammatory processes with particular regard for NLRP3 inflammasome in obese patients before and after bariatric surgery. In addition, we are studying the potential beneficial effects of probiotics or natural mixtures in counteracting the development of obesity and related comorbidities.
- Enteric glial NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to gut mucosal barrier alterations in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity (Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2024) D’Antongiovanni V, Fornai M, Colucci R, Nericcio A, Benvenuti L, Di Salvo C, Segnani C, Pierucci C, Ippolito C, Nemeth ZH, Haskó G, Bernardini N, Antonioli L, Pellegrini C. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39287080/
- Pathological remodelling of gut barrier as a prodromal event of high fat diet-induced obesity (Lab Invest. 2023). D’Antongiovanni V, Segnani C, Ippolito C, Antonioli L, Colucci R, Fornai M, Bernardini N, Pellegrini C. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37290605/
- Dietary Supplementation with the Probiotic SF68 Reinforces Intestinal Epithelial Barrier in Obese Mice by Improving Butyrate Bioavailability (Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023) Benvenuti L, D’Antongiovanni V, Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Bernardini N, Ippolito C, Segnani C, Di Salvo C, Colucci R, Martelli A, Flori L, Calderone V, Carta G, Ghelardi E, Calvigioni M, Panattoni A, Coppolecchia R, Arini A, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37099449/
- Dietary Supplement, Containing the Dry Extract of Curcumin, Emblica and Cassia, Counteracts Intestinal Inflammation and Enteric Dysmotility Associated with Obesity (Metabolites. 2023) D’Antongiovanni V, Fornai M, Benvenuti L, Di Salvo C, Pellegrini C, Cappelli F, Masi S, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36984850/
- The administration of Enterococcus faecium SF68 counteracts compositional shifts in the gut microbiota of diet-induced obese mice (Front Microbiol. 2022) Panattoni A, Calvigioni M, Benvenuti L, D’Antongiovanni V, Pellegrini C, Di Salvo C, Mazzantini D, Celandroni F, Fornai M, Antonioli L, Ghelardi E. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36590404/
- Targeting SIRT1 Rescues Age- and Obesity-Induced Microvascular Dysfunction in Ex Vivo Human Vessels (Circ Res. 2022) Mengozzi A, Costantino S, Paneni F, Duranti E, Nannipieri M, Mancini R, Lai M, La Rocca V, Puxeddu I, Antonioli L, Fornai M, Ghionzoli M, Georgiopoulos G, Ippolito C, Bernardini N, Ruschitzka F, Pugliese NR, Taddei S, Virdis A, Masi S. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35968712/
- Glomerular hyperfiltration in morbid obesity: Role of the inflammasome signalling (Nephrology. 2022) Moriconi D, Antonioli L, Masi S, Bellini R, Pellegrini C, Rebelos E, Taddei S, Nannipieri M. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35681274/
- Association Between Body Mass Index and Morbidity and Mortality During Hospitalization After Trauma (J Trauma Nurs. 2022.) Soliman SS, Durling-Grover R, Bilaniuk JW, Kong K, Renna L, Hakakian D, Rolandelli RH, Antonioli L, Nemeth ZH. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35275110/
- NLRP3 at the crossroads between immune/inflammatory responses and enteric neuroplastic remodelling in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity (Br J Pharmacol. 2021) Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Benvenuti L, Colucci R, Caputi V, Palazon-Riquelme P, Giron MC, Nericcio A, Garelli F, D’Antongiovanni V, Segnani C, Ippolito C, Nannipieri M, Lopez-Castejon G, Pelegrin P, Haskó G, Bernardini N, Blandizzi C, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34000757/
- Managing Obesity and Related Comorbidities: A Potential Pharmacological Target in the Adenosine System? (Front Pharmacol. 2021) D’Antongiovanni V, Fornai M, Pellegrini C, Blandizzi C, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33536924/
- Glial A2B Adenosine Receptors Modulate Abnormal Tachykininergic Responses and Prevent Enteric Inflammation Associated with High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity (Cells. 2020) D’Antongiovanni V, Benvenuti L, Fornai M, Pellegrini C, van den Wijngaard R, Cerantola S, Giron MC, Caputi V, Colucci R, Haskó G, Németh ZH, Blandizzi C, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32443525/
- Colonic dysmotility associated with high-fat diet-induced obesity: Role of enteric glia (FASEB J. 2020) Antonioli L, D’Antongiovanni V, Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Benvenuti L, di Carlo A, van den Wijngaard R, Caputi V, Cerantola S, Giron MC, Németh ZH, Haskó G, Blandizzi C, Colucci R. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32086846/
- Differential Impact of Weight Loss and Glycemic Control on Inflammasome Signaling (Obesity 2020) Antonioli L, Moriconi D, Masi S, Bottazzo D, Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Anselmino M, Ferrannini E, Blandizzi C, Taddei S, Nannipieri M. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32020775/
- Phytochemicals as Novel Therapeutic Strategies for NLRP3 Inflammasome-Related Neurological, Metabolic, and Inflammatory Diseases (Int J Mol Sci. 2019) Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Antonioli L, Blandizzi C, Calderone V. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31200447/
- Luteolin Prevents Cardiometabolic Alterations and Vascular Dysfunction in Mice With HFD-Induced Obesity (Front Pharmacol. 2018) Gentile D, Fornai M, Pellegrini C, Colucci R, Benvenuti L, Duranti E, Masi S, Carpi S, Nieri P, Nericcio A, Garelli F, Virdis A, Pistelli L, Blandizzi C, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30319424/
- Interplay between colonic inflammation and tachykininergic pathways in the onset of colonic dysmotility in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity (Int J Obes. 2019) Antonioli L, Caputi V, Fornai M, Pellegrini C, Gentile D, Giron MC, Orso G, Bernardini N, Segnani C, Ippolito C, Csóka B, Haskó G, Németh ZH, Scarpignato C, Blandizzi C, Colucci R. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30082748/
- Dietary flavonoids as a potential intervention to improve redox balance in obesity and related co-morbidities: a review (Nutr Res Rev. 2018) Gentile D, Fornai M, Pellegrini C, Colucci R, Blandizzi C, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29871706/
- The flavonoid compound apigenin prevents colonic inflammation and motor dysfunctions associated with high fat diet-induced obesity (PLoS One. 2018) Gentile D, Fornai M, Colucci R, Pellegrini C, Tirotta E, Benvenuti L, Segnani C, Ippolito C, Duranti E, Virdis A, Carpi S, Nieri P, Németh ZH, Pistelli L, Bernardini N, Blandizzi C, Antonioli L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29641549/
- Colonic motor dysfunctions in a mouse model of high-fat diet-induced obesity: an involvement of A2B adenosine receptors (Purinergic Signal. 2017) Antonioli L, Pellegrini C, Fornai M, Tirotta E, Gentile D, Benvenuti L, Giron MC, Caputi V, Marsilio I, Orso G, Bernardini N, Segnani C, Ippolito C, Csóka B, Németh ZH, Haskó G, Scarpignato C, Blandizzi C, Colucci R. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28808842/
- A2A adenosine receptors control pancreatic dysfunction in high-fat-diet-induced obesity (FASEB J. 2017) Csóka B, Törő G, Vindeirinho J, Varga ZV, Koscsó B, Németh ZH, Kókai E, Antonioli L, Suleiman M, Marchetti P, Cseri K, Deák Á, Virág L, Pacher P, Bai P, Haskó G. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28765173/